- Home
- All Courses
- Eco-Walks Learning Path
- Environmental Protection
Curriculum
- 2 Sections
- 2 Lessons
- Lifetime
- Introduction to Environmental ProtectionWelcome to Environmental Protection module. This is the first module in Eco-walks Learning Path which is an introduction to environmental protection. Environmental protection is about looking out for the places, creatures and spaces that need our help the most. It's about working together to find ways to bend our impact on the earth, a challenge that's more important than ever. That is why we invite you to learn more about the thing we all care for.1
- Biodiversity1
What is Biodiversity?
In module 2, we will learn more about biodiversity and why it is important for us.
Understanding biodiversity helps us with environmental protection, waste management, sustainable development, and climate change adaptations. Educating ourselves more about these issues will make us more aware during our outdoor activities. You will be learning more about each topic in the following modules. Now let us start with Biodiversity and its importance.
What is Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the different species of plants, animals, microorganisms, and the ecosystems in which they exist. It encompasses the genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity that exists at all levels of biological organization.
Biodiversity is crucial for several reasons:
Ecosystem Stability: Biodiversity contributes to the stability and resilience of ecosystems. Each species plays a specific role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem, such as nutrient cycling, pollination, seed dispersal, and pest control. A diverse ecosystem is better able to withstand and recover from environmental changes, such as natural disasters or climate fluctuations.
Ecological Services: Biodiversity provides numerous services essential for human well-being. These include clean air and water, soil fertility, climate regulation, flood control, and the production of food, medicine, and other resources. Many industries rely on biodiversity, such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and tourism.
Genetic Resources: Biodiversity is a vast reservoir of genetic information. Different species have unique genetic traits that can be harnessed for various purposes, including crop improvement, disease resistance, and pharmaceutical development. Preserving biodiversity ensures the preservation of these valuable genetic resources for future generations.
Despite its importance, biodiversity is under threat due to various human activities such as habitat destruction, climate change, pollution, overexploitation of resources, and invasive species. It is crucial to promote conservation efforts, sustainable practices, and responsible environmental stewardship to preserve and protect biodiversity for the benefit of current and future generations.
The Importance of Biodiversity
The health of our biological world, including our own health, depends on the functionality of the greater ecological system. This means that the availability of, among other things, proper air quality, clean water, and plant productivity, relies on steady ecosystem functionality. This also means that food production and our future nutritional security rely on the existence of many ecosystem functions. We take these functions for granted, but we should not.
Many functions are involved in maintaining healthy ecosystems. Among these functions are O2-CO2 gas exchange, nutrient cycling, such as nitrogen cycling, and energy flow between organizational levels along the food web. They are responsible for the stability of our biosphere. Therefore, it is clear that these ecosystem functions support our life and are thus crucial for our survival.
This also means that the components that construct and maintain the functionality of ecosystems are the basic elements that need to be protected.
What are these components?
Obviously, these are the plants and animals that comprise the ecological communities that provide the machinery for the ecosystem functions to exist.
As a metaphor, if a particular ecosystem resembles a car, then the plant and animal species are the cables, pipes, bolts and racks that enable its operation.
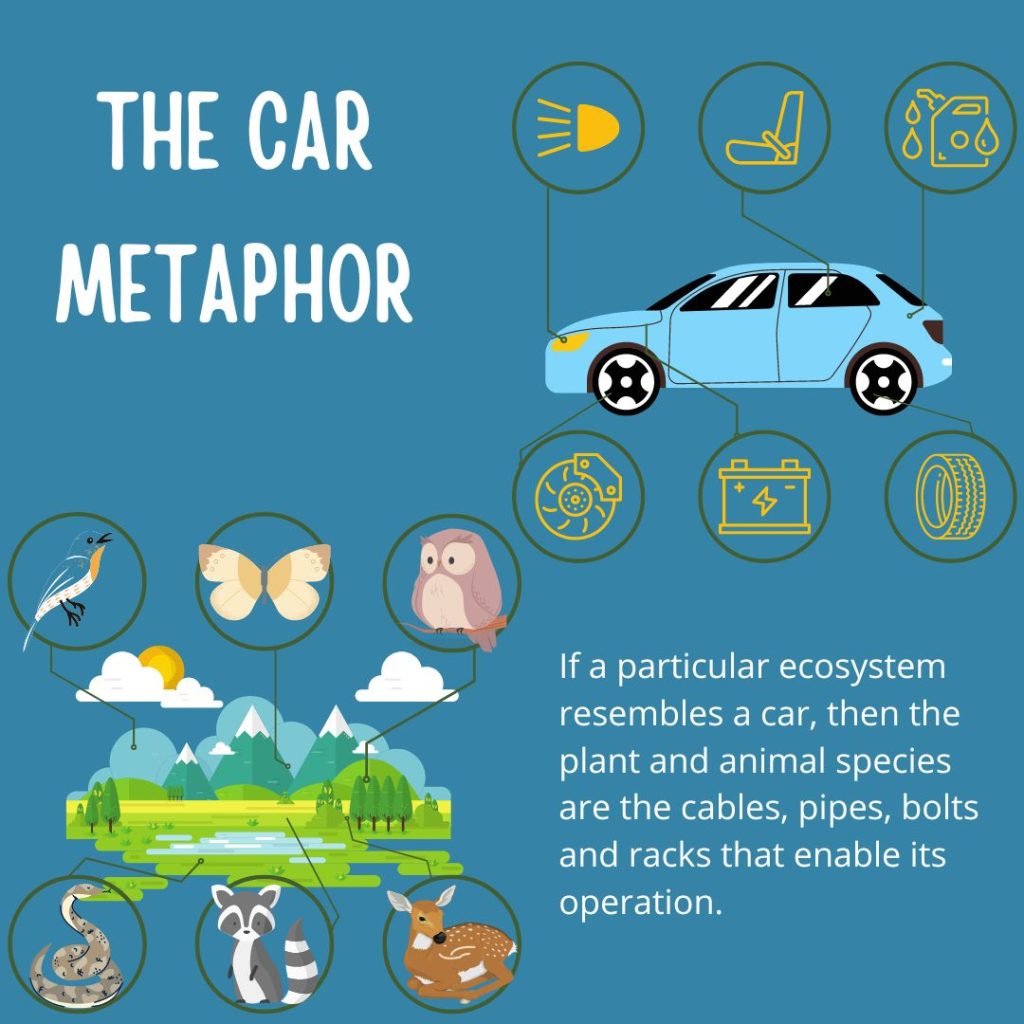
To persist, species need appropriate habitats, as well as the entire physical and biotic conditions in the ecosystem to which their habitats belong.
We use the term biological diversity, or biodiversity in short, to refer to all of these ecological elements.
The term Biodiversity had already been used by several ecologists in the 1960s and 1980s. However, the use of this term became even more popular following the Convention on Biological Diversity of the Earth Summit that was held in Rio de Janeiro in 1992.
Then, Biodiversity was defined as: “The variability among living organisms from all sources, including, inter alia, terrestrial, marine and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are part of.” This includes diversity within species, between species and of ecosystem. Practically, ecologists and conservation biologists refer to biodiversity as “diversity of diversities” with three major elements in mind: ‘Genetic diversity’, ‘Species diversity’ and ‘Ecosystem diversity’.
These elements reflect three major levels of organization in biology and, in a sense, provide the overall perspective on the need for diversity for the ecological functionality and stability.
Genetic diversity relates to the individual level, where the individual’s genetic load and variability among individuals provide some indication of the organisms’ ability to cope with certain environments and with future changes in these environments. Typically, the larger a populations is, the greater the genetic diversity found among its members, which is one of the reasons why large populations can cope better with environmental changes.
Species diversity relates to the community level; at this level, species abundance and richness reflect the interactions between the co-occuring species and with their physical environment. These interactions maintain the equilibrium and long-term balance between functional groups of species, such as decomposers, producers, and consumers, such as herbivores and carnivores.
Finally, ecosystem diversity refers to the different habitats and eco-physical environments where individuals of the different species in the community forage, survive, reproduce, and interact.
Activity:
In order to get some idea about species richness, the following exercise may help with realizing how much diversity (here, number of species) exists near our home. For example, most people are not aware of how many bird, mammal and reptile species live in their area or even within their own village or city. This is especially true for arthropods, such as spiders and insects.
1. Take a 30 minutes bird-watching walk where you live. Look for as many birds as possible. Increase your chance to see different bird species by choosing a route that goes through and near different environments (habitats), including within an urbanized area. Such different environments may include apartment complexes, between-buildings staircases, patio gardens, city gardens, avenues, etc.
2. Try to classify the birds you see – if you do not know what the species are, take pictures of them and/or write down details about each presumed species’ morphology (size, shape, wing-to-body length ratio, beak shape, etc.), color and behavior. Using local bird guides and/or by searching internet websites (nowadays the internet is full of bird-oriented information), try to identify the species. You can also contact a local birder for information.
3. Collect details on each bird species. Use local bird guides and/or internet websites:
Common name (Does it have a meaning?)
Latin name (Does it have a meaning? Who gave it its name?)
Abundance (Does it appear in pairs or several individuals or only seen singularly?
Occurrence (Have you seen it once or in several environments?)
Diet (What does it eat?)
Origin (Is it native to your area, or an invasive species? Was it as rare/abundant in the past or has its commonness changed recently?)
4. Upload your findings to this form. https://forms.office.com/e/wxfPAm4WFX
