- Home
- All Courses
- Eco-Walks Learning Path
- Sustainability
Curriculum
- 2 Sections
- 2 Lessons
- Lifetime
- What Is Sustainability?1
- What Can I Do to Live Sustainably?2
What is Sustainability?
Definition
In 1987, the United Nations Brundtland Commission defined sustainability as “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
This definition indicates the need to ensure the satisfaction of the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to satisfy their own needs.
In operational terms, this definition can be translated into three guiding principles:
the sustainable use of environmental resources must not exceed the capacity and timing of environmental restoration of these resources;
the sustainable use of non-renewable resources implies the extension of the life cycle of materials through recycling and replacement with renewable resources;
the emission of polluting substances and waste must not exceed the absorption capacity of the environment.
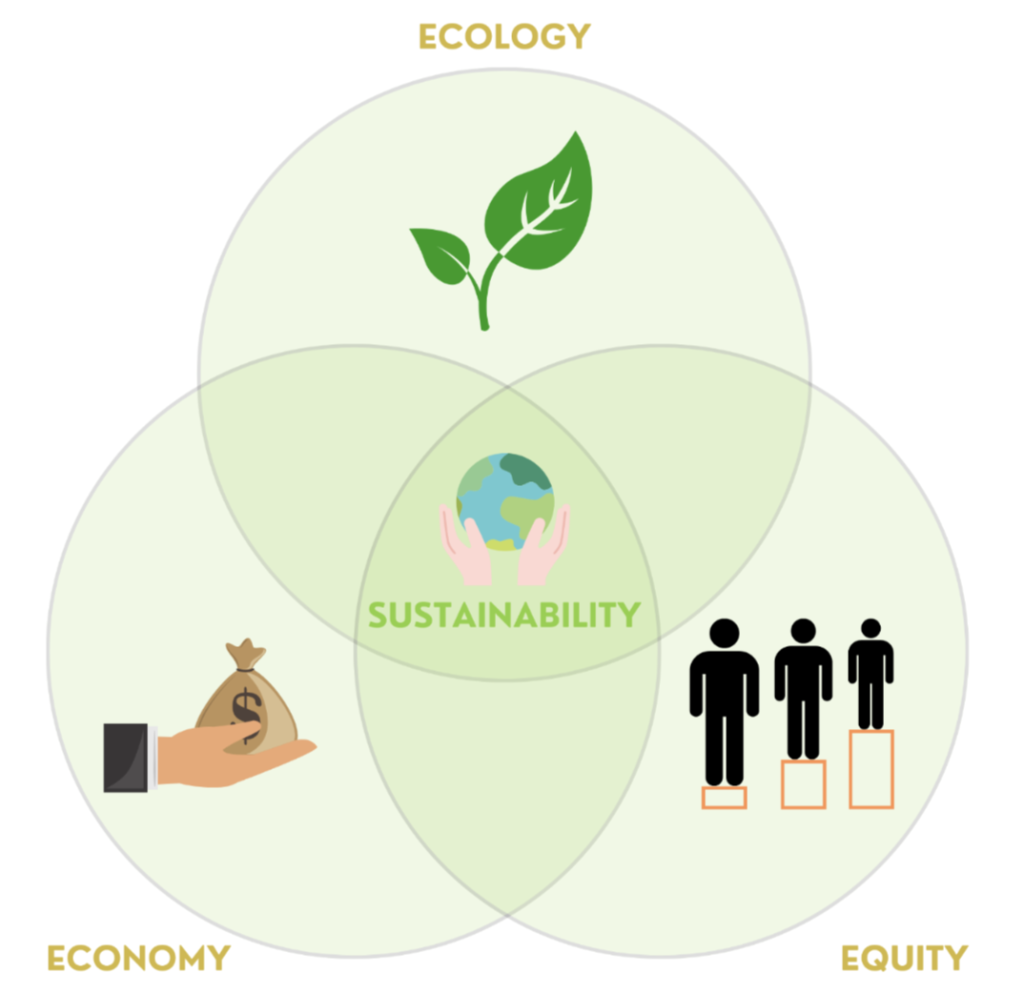
The 3 Es of sustainability
The 3 ‘Es of sustainability are Economy, Ecology and Equity. To achieve sustainable development, we need to find a balance between the three Es of sustainability. This means that sustainability is achieved when your actions are helping to develop the economy, promoting social equity, and protecting the integrity of the environment for future generations.
Video: What is sustainability?
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, was adopted by all 193 United Nations Member States in 2015. It is composed by 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), for a total of 169 targets, integrated and indivisible, which are an urgent call for action by all countries in a global partnership. They recognize that ending poverty and other deprivations must go hand-in-hand with strategies that improve health and education, reduce inequality, and spur economic growth – all while tackling climate change and working to preserve our oceans and forests.
Video: Do you know all 12 SDGs?
The ecological footprint
The ecological footprint (global footprint) is an indicator devised in 1990 by two Canadian researchers from the University of British Columbia, which serves to monitor the use of the ecological resources available on our planet by individuals, cities and nations up to the whole humanity.
The ecological footprint is calculated by relating the amount of food resources (for example, wheat, rice, corn, meat) and energy consumed with a value that corresponds to the area needed to produce these resources. The land area required to dispose of the waste produced is also taken into consideration in the calculation. The result is an area expressed in global hectares (one hectare equals 10,000 m2), which can refer to individuals, local communities or entire states.
Referring to Global ecological footprint, from the data collected it emerged that since the mid-1980s humanity has been living beyond its means in ecological terms, because the ecological footprint is greater than the global productivity of our planet. Calculations show that humanity currently uses the equivalent of 1.75 planets each year.
Activity
How many planets would we need if we all had your lifestyle? What is your personal Earth Overshooting Day?
Calculate your ecological footprint on: https://www.footprintcalculator.org/sponsor/FR/it
